Remote Control Slope Mower Enhancing Safety in Challenging Terrain Operations
Remote control slope mowers are transforming the way professionals manage steep, uneven and hazardous landscapes. As urban green spaces, agricultural terraces, highway embankments, solar farm slopes and riverbanks present increasingly complex mowing challenges, these purpose-built machines bring improved safety, efficiency and environmental benefits. Unlike traditional ride-on mowers or handheld tools used on inclines, remote control slope mowers allow operators to manage vegetation from a safe distance, reducing the risk of slips, falls and machine overturns while maintaining consistent cutting performance.
Understanding the Challenge of Steep Terrain Mowing
Working on slopes introduces several hazards and inefficiencies. Manual trimming is physically demanding and often unsafe on steep ground. Conventional ride-on mowers can lose traction or tip over on gradients, and heavy machinery may damage fragile soils or root systems. In addition, difficult access to remote embankments or conservation areas makes regular maintenance time-consuming and costly. These problems drive the need for a safer, more adaptable approach to vegetation control.
How Remote Control Slope Mowers Improve Safety
The primary safety benefit is distance. Operators can control the machine remotely, standing on stable ground away from the slope. This eliminates direct human exposure to unstable ground, hidden holes, loose rocks, or sudden drop-offs. Most remote slope mowers include emergency-stop features, automatic rollback prevention, and anti-tip geometry. These systems detect unsafe attitudes or loss of traction and either slow the machine down or cut power to the cutting implement, preventing accidents before they escalate.
Key Design Features That Enable Reliable Slope Work
Manufacturers design slope mowers with several technical features that make them suitable for harsh terrain:
• Low center of gravity and wide track bases to resist tipping.
• Tracked undercarriages or specially profiled tyres for superior traction on steep, wet or loose surfaces.
• Robust gearboxes and heavy-duty blades capable of cutting thick vegetation, brush and saplings.
• Remote transmitters with video feed options so operators can see what the machine is doing in real time.
• Fail-safe systems including automatic engine shutoff on loss of signal, roll sensors, and manual kill switches on the controller.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Benefits
Beyond safety, remote control slope mowers deliver operational efficiencies: one skilled operator can manage multiple units during a shift, cutting labor costs and downtime. The machines’ compact profiles reduce the need for heavy equipment mobilization and access roads, so projects begin sooner and with lower logistical costs. Fuel-efficient engines and focused cutting decks lower fuel consumption and maintenance intervals, reducing total cost of ownership for municipalities, utility companies, landscape contractors and agricultural managers.
Environmental and Practical Advantages
Because remote slope mowers are lighter and more maneuverable than tracked excavators or large ride-on machines, they cause less soil compaction and ground disturbance. This is crucial in conservation areas, sloped vineyards and embankments where erosion control matters. Quieter operation—especially from electric or hybrid models—reduces noise impact near residential zones and wildlife habitats. In addition, precise cutting reduces the need for herbicides, supporting integrated vegetation management and sustainability goals.
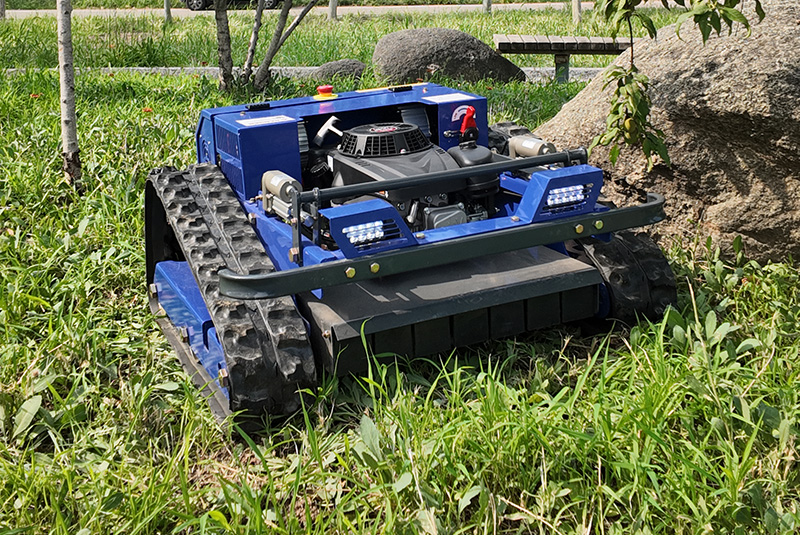

Typical Use Cases and Industries
Remote control slope mowers are used across a range of sectors:
• Transportation agencies for roadside and median maintenance along highways.
• Energy and utility firms to clear vegetation around substations, pipelines and solar arrays.
• Vineyard and orchard managers for inter-row and embankment mowing without risking vines or trees.
• Municipal park services for steep banks, ravines and waterways.
• Environmental contractors for invasive species control in sensitive habitats.
Remote Control Systems and Operator Interfaces
Modern remote control systems combine rugged wireless links with intuitive human-machine interfaces. Controllers often include ergonomic joysticks, tactile feedback, LCD or video displays and programmable presets for speed and blade height. Some systems stream a live camera feed from the mower, improving situational awareness. Advanced units feature geofencing and GPS integration to define work zones and record completed coverage for reporting and billing.
Safety Protocols and Best Practices
Even with remote operation, safe workflows are essential. Best practices include pre-job site assessments, establishing clear sight lines between operator and machine, using a spotter when visibility is limited, and maintaining robust communication (radio or mobile) between team members. Regular checks of signal integrity, emergency stops, and battery or fuel levels should be performed before and during each shift.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQs
Q How steep a slope can these machines handle
A Many modern remote control slope mowers are rated to safely operate on gradients of 30 to 50 degrees depending on track/tyre design and ground conditions. Always consult the manufacturer rating and perform a site assessment.
Q What happens if the controller signal is lost
A Most systems have a fail-safe that stops the engine or applies the parking brake on loss of signal. Some advanced models will execute a safe return to a pre-programmed zone.
Q Are there electric or hybrid options
A Yes. Electric and hybrid remote mowers are increasingly available, offering lower emissions and quieter operation—useful near residential areas and wildlife zones.
Q Can the machines cut woody brush or small trees
A Heavy-duty models with reinforced blades and high-torque gearboxes can handle woody vegetation up to a certain diameter; however, very large trees require chainsaws or mulchers designed for that purpose.
Q Is operator training required
A Yes. While user interfaces are made intuitive, proper training ensures safe operation, correct maintenance, and effective use of onboard safety features.
Integration with Smart Workflows and Fleet Management
For organizations managing multiple remote machines, telemetry and fleet management platforms enable centralized oversight. Fleet managers can monitor machine health, schedule preventive maintenance, track fuel or battery usage, and analyze productivity metrics. Integration with GIS and asset databases ensures that vegetation work aligns with broader infrastructure maintenance programs.
Case Example Real World Impact
A regional transportation department replaced manual trimming crews on embankments with remote slope mowers. Within one season they reduced worksite incidents by over 90 percent, cut manpower hours by 60 percent and eliminated the need to close lanes for roadside mowing—delivering clear public safety and economic benefits.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Routine maintenance keeps remote slope mowers reliable. Typical tasks include blade inspection and replacement, track or tyre checks, gearbox lubrication, battery health monitoring, and firmware updates for remote controllers. Manufacturers often provide modular components to simplify repairs in the field and minimize downtime.
Purchasing and Specification Guidance
When evaluating models consider slope rating, cutting width, traction system (tracks vs tyres), control range, video feed availability, powertrain (diesel, hybrid, electric), accessory compatibility (mulcher, flail, brush blade), and the availability of local service and spare parts. A pilot trial on representative slopes is highly recommended before committing to fleet acquisition.
Future Trends and Innovation Trajectory
The next generation of remote slope mowers will increasingly incorporate AI for obstacle recognition, autonomous path planning, and predictive maintenance based on sensor data. Advances in battery energy density and solar charging could enable longer electric operation windows, while improvements in lightweight materials will increase payload capacity without sacrificing stability.
Conclusion
Remote control slope mowers represent a significant step forward in safe, efficient vegetation management on challenging terrain. By removing operators from immediate risk zones, combining robust mechanical design with intelligent control systems, and offering environmental and cost advantages, these machines are becoming essential tools across multiple industries. As technologies mature, their role will grow further—helping organizations meet safety targets, reduce costs, and manage landscapes sustainably and effectively.
5. Get Your Personalized Solution Now
→ Call the selection hotline: +86 158 5359 8030 (also supports accessory customization inquiries).